Laser cutting has revolutionized the world of manufacturing and design, offering unparalleled precision and versatility. At the heart of this technology lies a crucial element: the array. Creating an array for laser cutting is an essential skill that can elevate your projects from ordinary to extraordinary. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of array creation, exploring techniques that will transform your laser cutting experience.
Understanding Arrays in Laser Cutting
An array in laser cutting refers to a systematic arrangement of multiple identical or related elements within a single design. This powerful feature allows for efficient production of multiple pieces in a single cutting operation, saving time and materials. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, mastering array creation can significantly boost your productivity and design capabilities.
| Key Array Concepts | Description |
|---|---|
| Repetition | Duplicating elements in a structured pattern |
| Spacing | Controlling the distance between array elements |
| Orientation | Arranging elements in various directions |
| Nesting | Optimizing material usage through clever arrangement |
| Parametric Design | Creating flexible arrays that adapt to changing variables |
For more information on laser cutting technology, visit: https://www.epiloglaser.com/how-it-works/laser-cutting/
Essential Tools for Array Creation
Before diving into the process, it’s crucial to equip yourself with the right software tools. Vector graphics programs like Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, or open-source alternatives such as Inkscape are indispensable for creating and manipulating arrays. These applications offer powerful features specifically designed for array creation and laser cutting preparation.CAD Software Advantages:
- Precise measurements and scaling
- Advanced array functions
- Compatibility with laser cutting machines
- Ability to create complex parametric designs
Step-by-Step Array Creation
1. Design Your Base Element
The foundation of any array is a well-designed base element. This could be a simple shape, a complex logo, or an intricate pattern. Ensure that your base element is optimized for laser cutting, with clean lines and appropriate detail level.
2. Determine Array Parameters
Before replicating your base element, consider the following parameters:
- Number of rows and columns
- Spacing between elements
- Overall dimensions of the final array
- Material constraints and machine bed size
3. Utilize Array Functions
Most vector graphics software offers built-in array or pattern replication tools. These functions allow you to quickly create grids, circular patterns, or custom arrangements with precise control over spacing and orientation.
4. Optimize for Material Efficiency
Clever array design can significantly reduce material waste. Consider these techniques:
- Nesting elements to maximize material usage
- Alternating orientation of elements to fit more pieces
- Incorporating shared cut lines between adjacent elements
5. Test and Refine
Before committing to a full-scale production, always test your array design. Create a small-scale prototype to verify spacing, alignment, and overall design integrity. This step can save time and materials in the long run.
Advanced Array Techniques
Parametric Arrays
For those seeking ultimate flexibility, parametric design offers a powerful solution. By linking array parameters to variables, you can create designs that automatically adjust based on input values. This approach is particularly useful for creating customizable products or adapting designs to different material sizes.
Multi-Level Arrays
Take your designs to the next level by incorporating arrays within arrays. This technique allows for the creation of complex patterns and textures that would be time-consuming to design manually. Experiment with combining different array types to achieve unique visual effects.
Dynamic Spacing
Instead of uniform spacing, consider incorporating dynamic spacing in your arrays. This can create visually interesting patterns or functional designs that change across the array. For example, gradually increasing spacing can create a sense of perspective or depth in your design.
Material Considerations
The success of your laser-cut array heavily depends on the material you choose. Different materials react differently to laser cutting, affecting the final result of your array.
Popular Laser Cutting Materials:
- Acrylic: Offers clean cuts and is available in various colors and finishes
- Wood: Provides a natural look but may require adjustments for grain direction
- Paper and Cardstock: Ideal for prototyping and delicate designs
- Metal: Requires more powerful lasers but allows for durable, precise cuts
When creating arrays for different materials, consider adjusting your design to account for material-specific characteristics such as kerf (the width of material removed by the laser) and minimum feature size.
Troubleshooting Common Array Issues
Even with careful planning, issues can arise when creating arrays for laser cutting. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
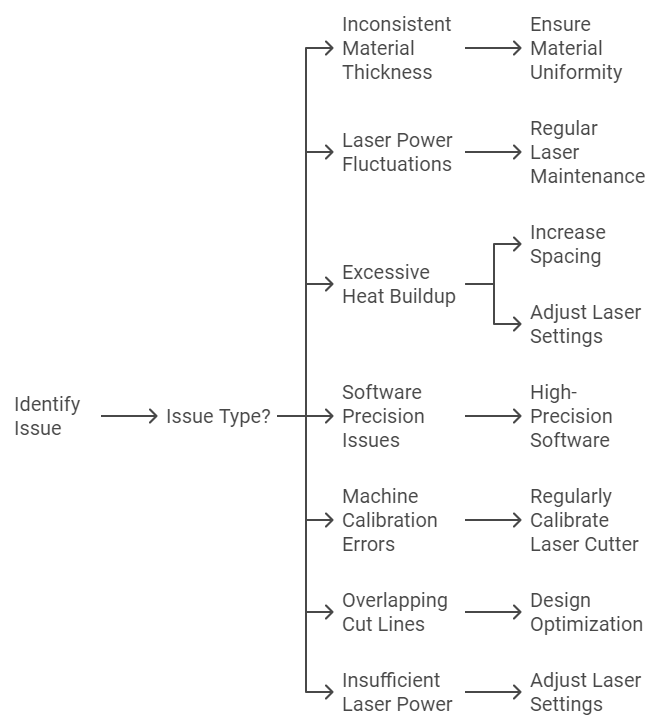
1. Uneven Cutting Depth
- Cause: Inconsistent material thickness or laser power fluctuations
- Solution: Ensure material uniformity and perform regular laser maintenance
2. Warping or Melting
- Cause: Excessive heat buildup in closely spaced arrays
- Solution: Increase spacing or adjust laser settings for faster cutting
3. Misalignment
- Cause: Software precision issues or machine calibration errors
- Solution: Use high-precision software and regularly calibrate your laser cutter
4. Incomplete Cuts in Complex Arrays
- Cause: Overlapping cut lines or insufficient laser power
- Solution: Optimize design to eliminate overlaps and adjust laser settings
Innovative Applications of Laser-Cut Arrays
The versatility of laser-cut arrays extends far beyond simple replication. Innovative designers and makers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with this technology.
Architectural Models
Architects are using laser-cut arrays to create intricate scale models of buildings and cityscapes. By arraying miniature structural elements, they can quickly produce detailed representations of complex designs.
Textile Design
Fashion designers are incorporating laser-cut arrays into their creations, producing fabrics with unique textures and patterns. This technique allows for the creation of delicate lace-like materials or bold geometric designs.
Interactive Art Installations
Artists are leveraging the precision of laser-cut arrays to create large-scale interactive installations. By combining arrays of moving parts or light-reactive elements, they’re producing immersive experiences that captivate audiences.
Custom Packaging Solutions
The packaging industry is benefiting from laser-cut arrays to create custom inserts and protective elements. This allows for precise fitting of products and adds a touch of sophistication to packaging design.
Sustainability in Array Design
As environmental concerns become increasingly important, designers are finding ways to make laser cutting more sustainable through clever array design.Eco-Friendly Practices:
- Maximizing material usage through efficient nesting
- Designing multi-functional arrays that reduce overall material consumption
- Incorporating biodegradable or recyclable materials into array designs
- Creating arrays that facilitate easy disassembly and recycling of products
The Future of Array Design in Laser Cutting
The field of laser cutting is constantly evolving, and with it, the possibilities for array design are expanding. Emerging technologies and techniques are set to revolutionize how we approach array creation.
AI-Assisted Design
Artificial intelligence is beginning to play a role in optimizing array layouts for maximum efficiency. AI algorithms can analyze designs and suggest optimal arrangements that human designers might overlook.
3D Laser Cutting
While traditional laser cutting focuses on 2D designs, advancements in 3D laser cutting are opening up new dimensions for array creation. This technology allows for the production of complex 3D structures through layered array cutting.
Integration with Other Technologies
The combination of laser-cut arrays with other manufacturing techniques is leading to innovative hybrid products. For example, arrays of laser-cut components are being integrated with 3D printed structures to create unique, functional objects.
Conclusion
Creating arrays for laser cutting is a skill that combines technical precision with creative vision. By mastering the techniques outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to push the boundaries of what’s possible with laser cutting technology. Remember that the key to success lies in continuous experimentation and refinement of your designs. As you gain experience, you’ll develop an intuitive understanding of how to create arrays that are not only functional but also visually stunning.Whether you’re crafting intricate jewelry, designing architectural models, or producing custom packaging solutions, the ability to create effective arrays will set your work apart. Embrace the challenges and opportunities that come with this powerful technique, and watch as your laser cutting projects reach new heights of sophistication and efficiency.

